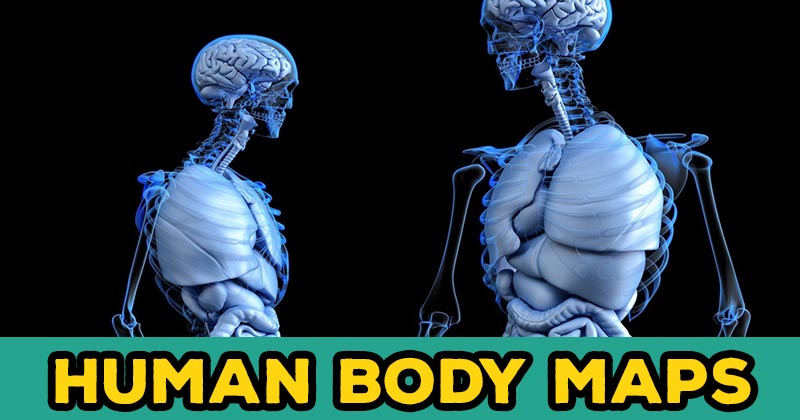
The human body is surely a fascinating substance to explore. In fact, its composition has its own features that make up your entire being. And if you’ve got a penchant for the human frame, this is a great way to fuel your curiosity. Here, you will know in detail the systems that work hand in hand every single day. Do take note that a body organ can be part of at least one system.
1. Circulatory system
The heart, lungs, arteries, blood, and blood vessels are the essential parts of the circulatory system. This relevant network powers the heart so it transmits oxygen and nutrients to the entire body. The circulatory system stops at various stations, from the lungs to the liver, kidneys, digestive tract, pancreas, and other significant organs. However, they move in one direction only to ensure the right process of transmission. Henceforth, it’s very important to keep your circulatory system healthy so blood vessels can provide a smooth-flowing transfer of oxygen and other vital nutrients.
2. Lymphatic system
Featuring a web of tissues and organs, the lymphatic system is apportioned to eliminate the unwanted resources in the body. The lymphatic vessels are likened to the veins and capillaries of the circulatory organs. From there, the lymphatic vessels are linked to the lymph nodes. Some of the most important parts of the lymphatic system are the tonsils, bone marrow, spleen, adenoids, and other lymphoid tissues. These transmit white blood cells to different organs to make sure that the body’s immune system is on tiptop condition. With the being said, the lymphatic organs serve as the interior armor of the human body to fight infection and get rid of toxins that cause diseases.
3. Nervous system
Next on the list is the nervous system, the structure assigned for your psychological functions. This consists of the brain, spinal cord, nerves, cells, meninges, and other sense organs. With its collection of nerves, it takes the responsibility of transmitting signals across different parts of the body. Simply said, it acts as the electrical wiring of the human body. For distinction, the nervous system is categorized into two―central and the peripheral. The former encompasses the brain and spinal cord while the latter involves all the nerves that open up from the two mentioned organs. These extend to the muscles and other key organs in the body.

4. Respiratory system
The anatomy of the respiratory system starts from the nose, down to the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and then the lungs. On top of the main respiratory organs, the muscles that take part in the breathing process are also included. Mainly, this system revolves around the transmission of oxygen from the first point of entry and throughout your body. And this process is called breathing. Aside from bringing oxygen to the human body, the respiratory organs also handle gas exchange to ensure the removal of waste gases such as carbon dioxide. Since the network is assigned to help you breathe and clean out unwanted gases, it’s crucial to take care of your respiratory system.
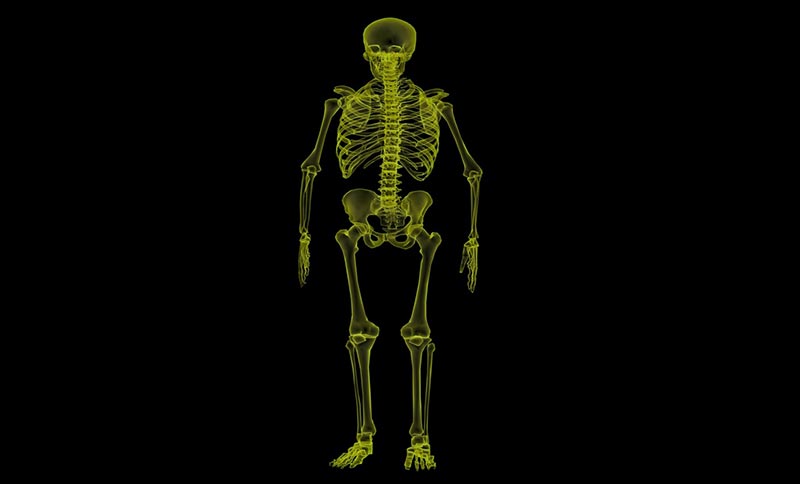
5. Skeletal system
A human body wouldn’t be complete without bones, joints, ligaments, cartilages, and other tissues. And these organs are the framework of the skeletal system. Each of these has its own function, from providing support, to protecting soft tissues, and even attaching muscle points. All in all, these organs help you with your body movements. Another interesting feature of the bones comprising the skeletal system is that these are actually living organs. This means that each bone is made of living cells, together with different minerals and protein fibers. And it is through the red bone marrow that new blood cells enter the bone.
6. Muscular system
The muscular system is more than just the physical muscles you can think of. This extends to three main types, namely skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscles are responsible for the conscious movements of your bones, which encompass different bodily activities such as exercising, eating, and the like. Smooth muscles, on the other hand, are those you can’t control voluntarily. These include intestines, ureters, prostate, as well as the walls of the stomach and blood vessels. Lastly, there’s the cardiac muscle or simply the walls that surround the heart.
7. Integumentary system
From hair to skin to nails, the integumentary system protects your body from physical damage and dehydration. More so, these organs help you with your senses so you continuously maintain homeostasis within your body. Aside from body protection and sensation, it also takes part in your body movement, temperature regulation, and excretion. And just a trivia―the skin is considered as the largest organ of the human body. An adult has around 8 pounds of skin or an area of about 22 square feet.
8. Digestive system
The digestive system is primarily assigned of the intake of food. But their function does not end there. They have to make certain that the food is transformed into nutrients so it will be relevant for bodily functions, growth, and even repair. Once the organs absorb the food nutrients, the digestive organs then ensure that food wastes are eliminated. To summarize the activities, it begins with ingestion, motility, digestion, absorption, and excretion. And the organs comprising this system are the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, intestines, rectum, and anus.
9. Reproductive system
The reproductive systems vary for male and female. And these consist of both internal and external organs that encompass the sexual process of the body. The primary function of the reproductive organs is to maintain the growth of species, hence the association of other systems in the body. The primary reproductive organs for males are the testes while for females are the ovaries.
10. Endocrine system
As the chemical messenger in the body, the endocrine system works hand in hand with other networks such as respiratory, digestive, and reproductive. They serve as a courier in regulating and secreting hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones then journey through various tissues to control bodily functions including mood, growth, metabolism, and reproduction. There are many endocrine organs and these are scattered across the human body. In the brain, you have the hypothalamus, pineal gland, and pituitary gland. From your neck down to your stomach, you’ll come across with the thyroid, parathyroid, and adrenals glands, together with the thymus and pancreas.
11. Urinary system
Eliminating body waste, filtering blood, and regulating body fluids―these are just some of the key tasks of the urinary organs. In addition, they help in controlling blood pH and electrolytes as well as in releasing hormones and extra salt. Often, the urinary system is also dubbed as the renal system as it consists of the kidneys, bladder, ureters, urethra, along with the renal pelvis. The kidneys, in particular, are tasked to filter blood and transmit excess fluid in the body, which is called as urine.
The relevance of the human body
Deep down the outer frame of the human body are bones, muscles, tissues, cells, blood, and other vital organs. Therefore, it’s important to take care not just of the physical aspect of your body but also its interior features. These body parts are the main reason why you are still alive, so nurture it properly and don’t take it for granted. Always remember that you’ve got one body and one life to keep.